Final Electron Acceptor in Aerobic Respiration
Sagittal Transverse Oblique Frontal What is illustrated by the recent discovery of taste receptors in the small intestine that detects sweetness. The oxygen molecule in aerobic respiration acts as the final electron acceptor resulting in the efficient production of ATP.
What Is The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Aerobic Cellular Respiration Quora
However some types of organisms.
. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A body has been sectioned in such a way that both lungs and the urinary bladder are visible. For example because erythrocytes red blood cells lack mitochondria they must produce their ATP from anaerobic respiration. However NAD can counteract the effects of some.
This oxygen is used in the mitochondria for aerobic respiration to produce ATP. Molecular oxygen is the most efficient electron acceptor for respiration due to its high affinity for electrons. The electron acceptor can be oxygen in aerobic bacteria but a variety of other electron acceptors organic and inorganic are also used by various species.
Cellular respiration is of two types ie. NAD is a coenzyme that is of critical importance to all body cells not only the brain. The molecular and cellular levels are of little.
The results of fermentation depend on the organic substrate most frequently carbohydrate or protein the applied catalyst in the form of either isolated enzyme or its microorganism producer as well as. The Krebs Cycle is responsible for the aerobic respiration of glucose derivatives fatty acids and protein to produce energy. This is an effective pathway of ATP production.
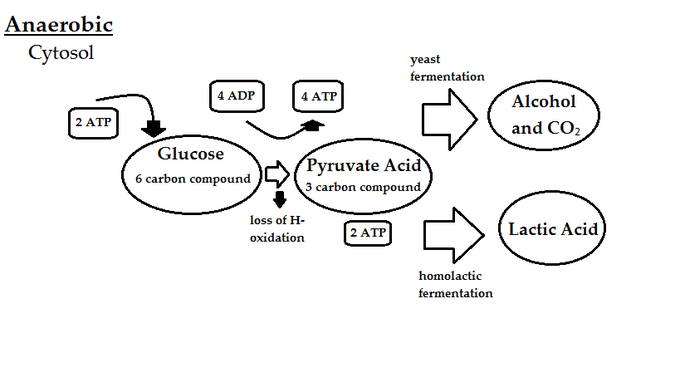
The efficiency of aerobic respiration is higher than the anaerobic one because the double bond in oxygen molecule assists the process of ATP production. For the electron transport chain to continue working there must be a final electron acceptor. In this reaction lactic acid replaces oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
If that acceptor is oxygen the process is considered aerobic respiration. Carbon dioxide is also produced in cellular respiration as a result of the oxidation of biomolecules. Aerobic bacteria such as the nitrifying bacteria Nitrobacter use oxygen to oxidize nitrite to nitrate.
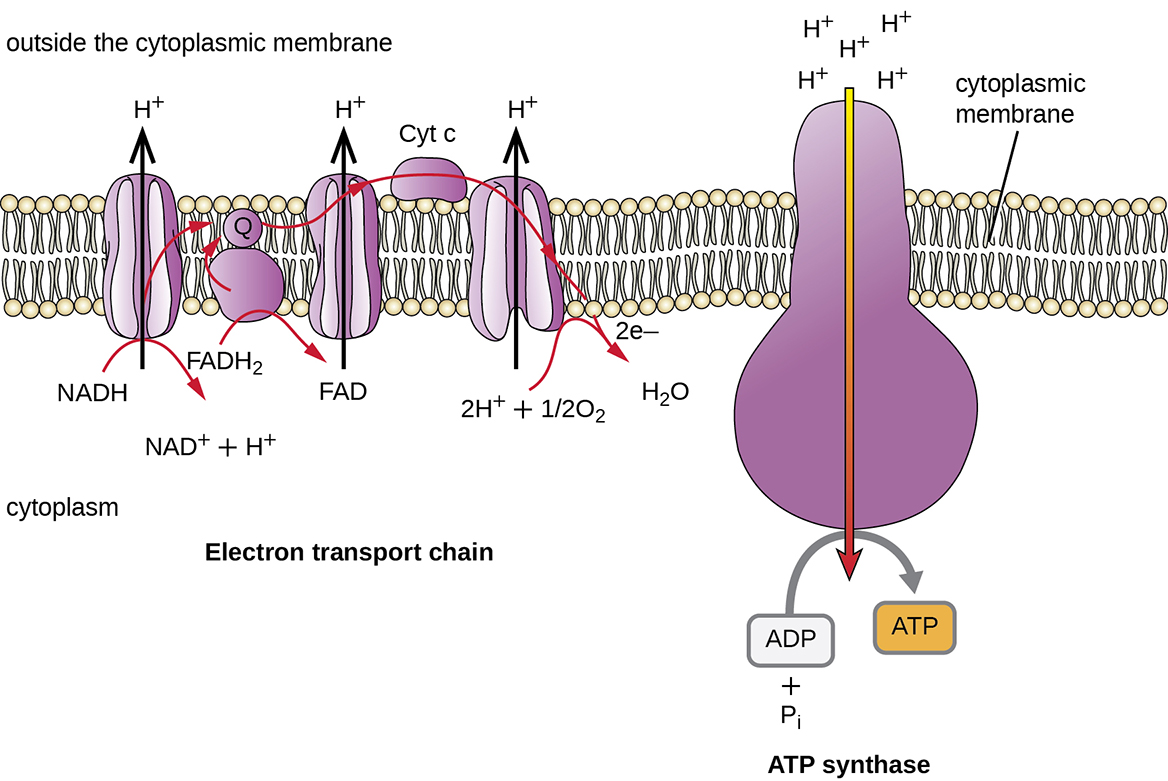
The oxygen is the final electron acceptor of what is known as the electron transport chain found in the last stage oxidative phosphorylation of aerobic cellular respiration. The terms aerobic respiration anaerobic respiration and fermentation substrate-level phosphorylation do not refer to primary nutritional groups but simply reflect the different use of possible electron acceptors in particular organisms such as O 2 in aerobic respiration or nitrate NO 3 sulfate SO 2 4 or fumarate in anaerobic respiration or various metabolic. Some lithotrophs produce organic compounds from carbon dioxide in a process called chemosynthesis much as plants.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in most cells of the body when oxygen is limited or mitochondria are absent or nonfunctional. Aerobic respiration is a much longer process that involves the exchange of oxygen. The electron carriers deposit the electrons at the beginning of the chain and then through a process called chemiosmosis produce many ATP.
Oxygen provides a force to drive the transport of electrons down the chain. What type of section was used. The process completes in an event known as oxidative phosphorylation where O2 is the final electron acceptor.
Fermentation may be defined as the generation of energy involving an endogenous electron acceptor from the bacterial enzymatic oxidation of any organic material. Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. It is also called fermentation.
This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration which relies on oxygen to produce energy. It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen. NADH is one of the final products of the citric acid cycle and is vital to brain health and functioning.
However some organisms have evolved to use other final electron acceptors and as such can perform respiration. It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP.

Biochemistry Pyruvate As A Final Electron Acceptor In The Electron Transport Chain Biology Stack Exchange

15 4 The Electron Transport Chain Chemistry Libretexts
8 3 Cellular Respiration Microbiology Canadian Edition

Introduction To Cellular Respiration And Redox Article Khan Academy

Electron Transport Chain Bioninja

5 9a Electron Donors And Acceptors In Anaerobic Respiration Biology Libretexts
Comments
Post a Comment